The foundation for the greenhouse: types of bases and instructions for making
The foundation is a reliable basis for any structure, and this is not an exception. Therefore, the majority of gardeners involved in the cultivation of crops, prefers to put them on a solid foundation. Such a design can be of any type and is mounted in accordance with the specifics of the structure.
When is it necessary?
Greenhouse is a multifunctional shelter that allows plants to provide the necessary conditions for their growth and development. In this regard, it must be safe in operation and serve a long time. When many different crops are grown on a land plot, the installation of a stationary structure on the foundation is considered the right decision. Of course, you can plant vegetables and just in the open ground under the film, saving on the cost of building such a base, but then problems may arise.
The film is made of lightweight material, therefore it is not able to withstand strong wind gusts, and the design is easily deflated.
As for buildings consisting of glazed frames, in which metal fins are put to increase rigidity, they are characterized by high mass and density, provide plants with reliable protection from the negative effects of the environment. Such structures are not built without a foundation, since it serves as a support for the upper parts of the structure. The base for stationary greenhouses is usually made of reinforced concrete, stone, brick or timber, its choice depends on the material from which the main parts of the structure are assembled. In addition, laying the foundation, it is possible to increase the height of the walls, and this allows you to expand the area inside the building and plant more crops.
Functions
The foundation in greenhouses is the main component, since it performs many functions. It well maintains the enormous weight of the structure and makes it much more stable, provides the structure with independence from atmospheric effects and underground moisture.Thanks to this installation, the operational period of the greenhouse is extended, since it is completely isolated from the soil surface and is not subject to destruction. In addition, the building’s energy efficiency and protection from insects and pests is significantly improved.
The crop reliably hides in the shelter, it is not threatened by the penetration of cold air flows, indoors creates the optimal climate for the development of crops.
Requirements
Before placing a greenhouse on the plot, it is necessary to lay a solid foundation. It can be made using various technologies using any material.
Choosing the appropriate type of base, you should consider some of the nuances.
- The size of the building. The greater its area, the more robust the installation is. This is especially important if the dimensions exceed 40x40 m.
- Characteristics of the soil where the planned installation of the structure. For this, the type of soil, the depth of its freezing and the passage of groundwater are determined in advance.
Since the foundation will serve as the main protection for the building, it must necessarily meet the following requirements:
- to be highly resistant to the negative influence of the external environment, this is especially important in the spring, when groundwater rises in level and snow melting is observed;
- be resilient in supporting the structure and frame, strengthen it and withstand the weight of the structure;
- provide indoor climate suitable for growing plants;
- to be made of high-quality building material in order to fulfill all its functions as much as possible.
Kinds
At the moment when installing greenhouses most often used strip, slab, columnar and pile foundation. The choice of one or another type of base is determined in each case individually, depending on the climatic zone, the terrain, the soil properties and the dimensions of the structure. Each type of foundation has its own characteristics.
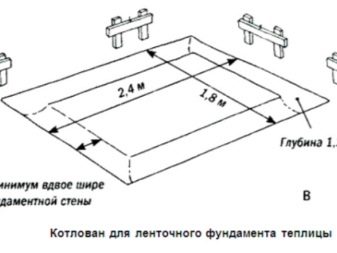
Tape
It is the most common option for all types of buildings.
Such a base may differ in construction technology.
- For construction on fertile and hard ground, it is made unburied, removing only the top layer of earth. In many cases, this basis is used when you need to install screw piles on the columns of pipes.
- Shallow-depth requires digging a trench to a depth of at least 800 mm, therefore it is not suitable for areas where there is a high groundwater flow.
- As for the recessed, it is placed at a depth of 1.4 m. This basis is considered to be durable and reliable, the disadvantage is that the cross-section and height must be accurately calculated during construction.
As a rule, the construction is erected, observing the proportion of 1.5-2 / 1, where the first indicator is the length and the second is the width. In order to get the foundation warm, it is important for the tape to choose the right material.
This may be a conventional reinforcing frame, filled with cement mortar, or concrete, lined from ready-made solid blocks, connected by metal fittings. Often, such a base is made of concrete, filling it with foam block or brick construction; it is also possible to install it from tires, bottles, sleepers and wood.
To install a non-buried tape used timber on concrete supports. But since the wooden base is unstable to the negative effects of external conditions, moisture is quickly absorbed and can rot or become covered by fungus,Before installation, it must be well treated with a special protective mixture, additionally coated with engine oil or pasted over with sheets of roofing material.
Slab
In contrast to the previous type, such a device is ideally suited for the structure of stationary greenhouses on sites with sand, unstable soil and elevated groundwater levels.
The slab foundation is of two types:
- floating - concrete pavement is placed directly on the soil surface;
- combined - when foam blocks are placed in a 70 cm deep pit on a sandy pillow or are prepared separately as a filler frame.
Compared to the tape construction, tiling is done without short circuit around the contour. The thickness of the base for light buildings should not be less than 100 mm, and for stationary winter 200-250 cm.
This foundation is characterized by durability and well provides the design with stability, isolating its internal space from pests and cold.
Despite such advantages, such an installation is expensive, as it requires additional insulation and laying of the drainage system.
Columnar
It is the most budgetary option for laying of a basis under the greenhouse.Metal poles or asbotrub are buried to a depth of 80 cm, keeping a distance of 2 m between them. If the greenhouse is small, then its foundation can not be sunk into the soil. In addition, when erecting a columnar base, masonry made of side stone or brick is also used. Can be additionally used ready-made concrete pillars, they are installed, then reinforced and poured concrete.
Wooden stumps and foam blocks are also ideal for non-buried designs.
The main disadvantage of the columnar foundation is the presence of gaps that form between it and the soil level, they cause cold air to enter the greenhouse. In order to prevent this, as well as to ensure the construction of an appropriate microclimate for growing crops, in this case it is recommended to perform warming in the form of boarding or brickwork.
Pile
It is an ideal choice for the construction of large greenhouses in a relief and marshy area. It is placed below the level of freezing of the earth, at a depth of at least 30 cm.
There are two types of piles:
- screw - supporting elements equip blades and placed in the ground with the help of special equipment or a drill;
- zabivny - channel, sleepers or pipes are clogged in the ground.
The main advantage of the pile foundation is that its installation takes place without concrete work, so the time to assemble the structure is significantly reduced.
As for the shortcomings, it is difficult to make such a basis yourself. Since any violation of the geometry can lead to support deformations, the installation is best to be trusted by experienced professionals.
Piles must be placed, observing a step of 2 m. During construction, their upper tips are sawn to the required size, and then they are connected by a grillage, which further ensures the strength and integrity of the structure. As a grillage, a wooden bar, sleepers soaked in engine oil or a plastic column can be used.
Which is better to choose?
The greenhouse can be purchased as a finished product, and independently assembled from film, old window frames and metal structures. As for the foundation, then the question of its construction should be taken responsibly, taking into account not only the material and size of the building, but also the climatic conditions and geodetic conclusions.
The following expert recommendations will help you to make the right choice in favor of one or another type of foundation:
- in the case when it is planned to put a small greenhouse with minimal construction costs, it is best to give preference to a wooden base, or install it on steel anchors;
- for sites located in harsh climatic conditions on a small slope, a pile or pillar foundation is ideal;
- so that the greenhouse construction, located next to the residential building, harmoniously combined with its design, a tape, brick or stone base would be a good option;
- For heaving soil, a pile or slab foundation is considered an ideal choice;
- under the glass buildings usually lay the basis of the ribbon.
How to do it yourself?
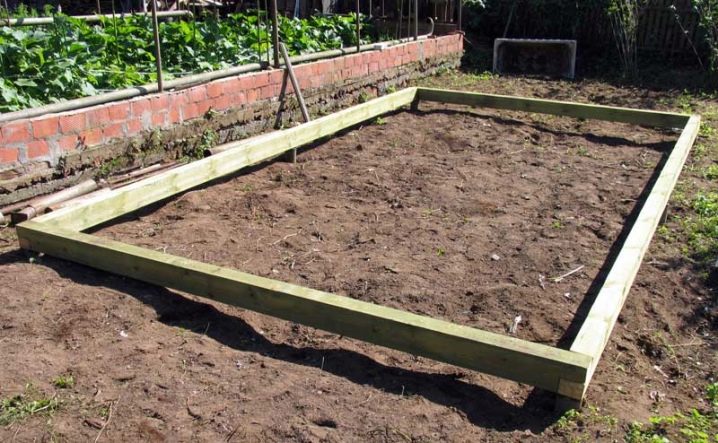
The installation of the greenhouse and the foundation for it is considered a time-consuming process, but with all the necessary materials and a great desire, even an inexperienced builder can cope with this task. To do this, newcomers are encouraged to choose the easiest option - the foundation of the timber. To install the structure yourself, you need to initially prepare a timber, its sides should not be less than 10 cm. On the land plot, appropriate markings are made,during which you need to strictly observe the geometry of the corners. Then you should level the platform, dig a trench and carry out the fastening of the beam.
Since wooden elements are placed in the soil at half their thickness, then to protect the material from moisture, beams are necessarily hammered with roofing material or covered with mastic. The depth of the bookmark may vary depending on the design parameters of the greenhouse. The skeleton thus obtained is fixed additionally with staples; this should be done in order for it to acquire strength. After that, you can mount the building on the timber.
If you need a strong foundation for a stationary greenhouse, then it should be installed from the blocks. It will reliably protect the structure from external influence and allow it to fulfill its functions to the maximum. Since the blocks are characterized by good waterproofing performance, they are ideal for building on soil with high humidity.
To make the base durable, with its tab, the following step-by-step instruction is used:
- the plot is prepared first, and markings are applied under the base;
- then in those places where the corners will be located, for accuracy wooden pegs are driven in and the thread is pulled;
- a trench is dug up to a width of 30 cm, its depth must be greater than the level of soil freezing;
- the bottom of the site is covered with a small layer of gravel in 10 cm;
- concrete is being poured, and blocks are placed on the frozen solution;
- Finally, the surface is flattened and cleaned, the joints are closed with cement mortar.
The brick-concrete foundation is also very popular when installing greenhouses. Bricks laid on a concrete surface, are an excellent support for the construction. But this option is not used for buildings in which crops are grown all year round, as the foundation is laid shallow and poorly protects them from freezing the land.
It is easy to make this foundation: you first need to dig a trench to a depth of 10 cm and a width of not more than 20 cm, then put solid formwork, pour concrete and put a plank on top of the entire perimeter.
The final stage in the work will be the installation of anchor bolts with a diameter of 12 mm, they will further strengthen the frame.After complete drying of the foundation, brickwork is performed. It is important to pay attention to the fact that the placement of the bolts coincided with the joints of the bricks, they are then sealed with concrete solution.
For more experienced craftsmen, the laying of a slab foundation, which is considered the most durable and durable, is suitable. It will not only protect the greenhouse from pests and water, but also allow inside its premises to create the most comfortable conditions for growing plants. The difficulty of mounting such a base lies in the exact calculations and laying of the drainage system, which allows to drain excess water through special holes.
Installation works are carried out in several stages:
- the ground is being prepared and markings are being applied;
- over the entire area of the future building, there is a ditch digging a depth of 30 cm and enclosed with formwork;
- the bottom of the pit is first covered with a layer of wet sand, then with gravel, everything is thoroughly tamped down;
- Reinforcement is performed using a mesh.
- inside the frame is poured with concrete, and after it hardens, anchor bolts are attached.
In some cases, greenhouses are installed only for the season, so their base does not need to be made durable.In such situations, a point foundation is used - it does not require time and money, is simple in construction and well protects the structure not only from pests, but also from weeds.
The procedure for its construction is as follows:
- the area where you need to locate the greenhouse is planned, and in the corners they drive in small bollards, pre-impregnated with an antiseptic;
- around the perimeter of the future building wooden poles are hammered, keeping a distance of 1 m between them;
- on the ready-made supports fix the building corners, and the frame of the structure is mounted.
All the above options for the installation of the foundation involve the use of high-quality building materials, but often in search of an alternative replacement, many gardeners prefer to choose a cheaper material that is always at hand and characterized by high performance characteristics. The most common in this case is the foundation of glass bottles, while they must be empty, and if the concrete solution gets into the container, it is removed.
Installation is performed as follows:
- first of all, along the perimeter of the plot, a trench is dug to a depth exceeding the freezing of the soil and up to 30 cm wide;
- the resulting recess is poured with concrete solution, bottles are placed horizontally in it;
- then a thin layer of mortar is re-poured on top, then a wooden formwork 30 cm high is mounted;
- in the last layer of the mixture, the bottles are placed again so that their neck is placed inside the future greenhouse;
- concreting is continued until the height of the base is equal to the upper line of the formwork;
- at the end the surface is carefully leveled and cleaned.
On how to properly establish the foundation for greenhouses, see the following video.